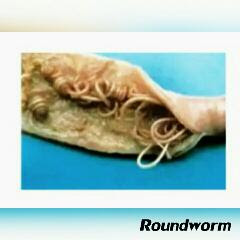
Nervous Signs And Lameness

This is the type of muscular disease that mainly affect the poultry limbs (wings and legs) and disallow free movement of chicken from one place to another. It is sometimes refers to as Locomotor disease. Signs in sick chickens Signs may vary, but usually chickens lie down because they cannot stand erect. They are reluctant to move or limping when movement is compulsory. Nervous signs may include staring into the sky for not knowing where they are, pulling the head and neck over their backs, paralysis and sores on the breast muscles from lying down. Other signs are crooked toes, swollen hocks, hyper-extended or rubbery legs. Causes There are many different types of organisms that can cause nervous signs and lameness. These include: * Bacteria (Salmonella, Botulism) * Viruses (Newcastle disease, Mareks disease, avian encephalo- myelitis) * Fungi (Aspergillus) Treatment A complete hygiene and disinfection programme should be planned together with the animal health technici...